A collection of useful resources for determining and dealing with the source of 100% CPU usage problems, which cause the system to become unresponsive either intermittently or continuously.
Note that the System Idle Process is supposed to have a high CPU usage rate at idle. This process accounts for unused system time. If your system is responsive and the System Idle Process CPU usage is high, then you do not have a CPU usage issue.
 |
When you move a Dynamic connector shape to a different connection point on a shape in your cross-functional flowchart, you may receive an error message similar to one of the following:
Microsoft Visio C++ Runtime Library
Runtime Error!
Program: Drive:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\Visio10\Visio.exe
abnormal program termination
Or
The instruction at "0x30b26b70" referenced memory at "0x1a5a01b4". The memory could not be "read".
Click on OK to terminate the program.
When you click OK, Visio stops responding (hangs).
Additionally, when you start Task Manager (press CTRL+ALT+DELETE, and then click Task Manager, and then click the Processes tab, the Visio.exe process may consume up to 100 percent of CPU resources.
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
If you put a laptop computer in standby and resume it repeatedly while the computer is using battery power, the processor may remain at full power until you restart the computer. This problem occurs only on computers with processors that support multiple power-consumption states.
 |
|
|
 |
Provides a fix for a problem in Windows XP where CPU utilization reaches 100 percent when you run programs after you install Windows XP Service Pack 2.
 |
|
|
 |
This article describes how to resolve 100% CPU usage by the csrss.exe process when the user's profile is corrupt.
 |
|
|
 |
After you install Windows XP Service Pack 1 (SP1), CPU usage may reach 100 percent under some battery conditions. Service pack information Windows XP322389 How to obtain the latest Windows XP service pack.
 |
 |
 |
 |
When you print on an LPT printer port, 100 percent CPU usage occurs until the print job is completed. This slows down other programs until the print job is completed. In some case, other programs may slow down enough that they seem completely unresponsive. This behaviour affects all power users who have many programs running at one time.
 |
|
|
 |
The animation in the Tasks pane in Windows Explorer may cause 100 percent CPU usage when you right-click an item that is not selected. To work around this problem, select the item before you right-click it.
 |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
 |
Describes a problem where you run a WinSNMP program that listens for traps and 100 percent of your CPU usage is consumed on your Windows XP-based computer.
 |
|
|
 |
On a Microsoft Windows XP-based or Microsoft Windows Server 2003-based computer that uses a removable memory storage device, you may find that, in certain situations, CPU usage in the Indexing Service (Cisvc.exe) increases to 100 percent.
 |
|
|
 |
Fixes a problem where the System Monitor (Smlogsvc.exe) uses 100 percent of CPU after two days. To resolve this problem, you must install a hotfix.
 |
 |
 |
 |
If you resume your computer from hibernation after you remove the computer from a docking station, the computer may seem to stop responding (hang), and Windows Task Manager may show 100 percent CPU usage until you reboot the computer.
 |
|
|
 |
When you unplug a Universal Serial Bus (USB) microphone, you may experience any of the following symptoms: A program that is currently using the microphone (such as Microsoft NetMeeting, GraphEdit from the Microsoft DirectShow SDK, or AmCap).
 |
|
|
 |
Fixes a problem that may occur if you have an "Incoming Connections" network connection defined. Provides a hotfix to resolve the problem. You must have Windows XP Service Pack 2 installed to apply the hotfix.
 |
|
|
 |
Fixes a problem with the Helpsvx.exe process that exhausts your computer's resources and causes your computer to stop responding when you start Help and Support.
 |
|
|
 |
In Windows Explorer, when you right-click a file or folder, you may experience any of the following behaviour:
Any file-copy operation that is occurring at that time may appear to stop responding. Network connection speed may significantly decrease; All streaming input/output operations are degraded. For example, streaming audio over Windows Media Player becomes distorted.
 |
 |
 |
 |
When you install RealNetworks RealOne Player on your computer, you may experience decreased computer performance. For example, it may take a longer time than expected for Windows to load when you start your computer. Additionally, when you open Task Manager (press CTRL+ALT+DELETE, and then click Task Manager) and then click the Processes tab, you may find that the Evntsvc.exe process uses up to 100 percent of CPU resources.
 |
|
|
 |
When you use a Visioneer universal serial bus (USB) scanner, your computer may experience a sudden, unusually high amount of CPU usage. After the scanner is installed, Task Manager may report that the service host program (Svchost.exe) utilizes 10 to 30 percent of the CPU. However, when you disable the scanner by using Device Manager, the unusually high amount of CPU utilization is stopped (and lowered).
 |
|
|
 |
If you repeatedly select an item that is in a Combo box in a custom program that retrieves information from a server, the server may stop responding. Additionally, the Microsoft Windows XP-based client computer may use 100 percent of its CPU resources.
 |
|
|
 |
When you try to install a product update (for example, a security patch, a critical update, an update rollup, or a hotfix) for [Windows XP], the installation may stop responding (hang).
When this problem occurs, the Processes tab in Windows Task Manager may indicate that Update.exe is using most or all the CPU resources. To start Windows Task Manager, right-click an empty area on the taskbar, and then click Task Manager.
 |
|
|
 |
You use the Enabled Languages Kit (ELK) to configure a Microsoft Windows XP-based computer to use a new language locale. After you do this, CPU use may reach 100 percent. Additionally, the computer may stop responding. This problem occurs when an external CD or DVD drive is detected.
 |
 |
 |
 |
The processor performance state may not be restored to the maximum state if the CPU runs at 100 percent. This problem occurs if the computer is 100 percent busy when the power policy changes.
 |
|
|
 |
You are using a Microsoft Windows XP Media Center Edition 2005-based computer. The computer may become slow or unresponsive if you connect an empty USB flash drive when the mouse pointer is located over an option in Online Spotlight. The Processes tab in Windows Task Manager shows that the Ehshell.exe process is using a very high percentage of CPU resources. The computer returns to typical operation after about ten minutes.
Note This problem occurs only the first time that you connect the drive during the current session of Windows.
 |
|
|
 |
When you use Microsoft Visual Basic for Windows 6.0 on a Microsoft Windows XP-based computer, if you view the properties windows of a Visual Basic form, click Font, and then click the ellipsis button (...) to try to change the font properties, the font window only partially appears, and the Visual Basic IDE stops responding. When this problem occurs, the VB6.exe process uses 100 percent of the CPU.
 |
|
|
 |
Under some conditions, your computer may run slowly. This behaviour can occur for any of the following reasons:
- Programs may be started automatically when you start your computer. Programs that run when you start your computer typically run all the time; this uses a portion of your computer's system resources that cannot be used for any other task.
- You may be running a program that creates memory leaks. When you quit a program, the system resources that the program uses should be returned to the operating system. However, some programs do not return all of these resources, effectively "leaking" memory, and this can create a low system-resource state.
- Your computer may have a small or minimal amount of random access memory (RAM), or a slower central processing unit (CPU). For example, although Windows XP can run with a minimum of 64 megabytes (MB) of RAM, this amount of RAM may not be sufficient to maintain a high speed while you run one or more programs.
|
|
|
 |
Computers that are equipped with multiple processors that support processor power management features, such as Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) processor performance states, require Microsoft Windows XP Service Pack 2 (SP2). Additional updates are available to optimize performance and behaviour on computers that are running Windows XP SP2. Without these updates, computers that are equipped with these power management-capable, mobile, dual-core processors may experience decreased performance or unexpected behaviour.
Note This problem also applies to x64-based versions of Microsoft Windows Server 2003. However, this article and its associated private hotfix are not intended to resolve timing problems in games and other applications that run on AMD dual-core computers.
 |
 |
 |
 |
Consider the following scenario. You are running antivirus software on the computer. Either of the following actions occurs:
- The Wsusscan.cab file or the Wsusscn2.cab file is copied to a local computer.
- The Wsusscan.cab file or the Wsusscn2.cab file is copied from a folder on a local computer to a different folder on the same local computer.
Note The Wsusscan.cab file or the Wsusscn2.cab file may be copied by Microsoft Systems Management Server (SMS) or the Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer (MBSA) to perform an offline security scan. After either of the previous actions occurs, you may experience one or more of the following symptoms:
- CPU use may increase to 100 percent.
- The computer may be slow to respond.
- The computer may appear to stop responding.
- Virus scanning may take a long time.
- The virus scanning process may quit or may time out.
- System resources may become low and may not be recoverable.
Note: The symptoms that you experience depend on the antivirus software that you are using and the scan options, such as scanning inside archived files, that you have configured.

|
|
|
 |
When you click a large Audio Video Interleaved (AVI) file in Windows Explorer, Microsoft Windows may stop responding (hang). Additionally, when you view the Processes tab in Windows Task Manager, you notice that the Explorer.exe process consumes 100 percent of CPU usage for up to two hours or more.
 |
|
|
 |
When you install RealNetworks RealOne Player on your computer, you may experience decreased computer performance. For example, it may take a longer time than expected for Windows to load when you start your computer.
Additionally, when you open Task Manager (press CTRL+ALT+DELETE, and then click Task Manager) and then click the Processes tab, you may find that the Evntsvc.exe process uses up to 100 percent of CPU resources.
 |
|
|
 |
When you attempt to add a counter, System Monitor may stop responding (hang), and CPU utilization may increase to 100 percent. This problem can occur only if a disk upper-filter driver is installed, where the driver name is 8 characters long, and is not equal to "diskperf".
 |
|
|
 |
When you install Windows XP on a computer that uses an ASUS P2B motherboard, the computer may stop responding (hang). The Processes tab in Task Manager may show that the CPU is using 100 percent of the system resources.
 |
 |
 |
 |
Consider the following scenario. You install Microsoft Windows XP on a computer, and then you run the Defrag. exe command-line tool to defragment the hard disk of the computer. However, the deragmentation [sic] process operation does not successfully finish. Then the Defrag.exe tool stops responding (hangs). Additionally, when you open Task Manager, you notice that the CPU usage for the Defrag.exe process increases to 100 percent and stays at that level.
 |
|
|
 |
You experience a delay when you transfer data over a USB port on a computer that is running Microsoft Windows XP with Service Pack 2 (SP2). For example, you experience a delay of five seconds before the data transfer is completed. When this problem occurs, CPU usage increases to 100 percent.
 |
|
|
 |
After you upgrade the domain to Active Directory, existing Windows 2000-based computers and Windows XP-based computers may not be updated to the DNS-style domain name. As a result, the servers may not receive a Kerberos ticket. If you investigate the computer account attributes for the affected computers by using LDIFDE, the dNSHostName property and the servicePrincipalName property are left blank. If you turn on auditing for logon failures, a security event ID 675 message ("Pre-authentication failed") is intermittently logged for the affected computers. Users may receive the following error message:
The system cannot log you on now because the domain domainname is not available.
If many domain members experience this problem, you may notice that your CPU usage approaches 90% to 100% when computers change their password. The computers then send Kerberos AS requests that fail with a "Pre-authentication failed" error. This problem drives up the CPU load on the domain controllers, especially the primary domain controller emulator, because by default, the domain controllers forward these requests to the primary domain controller.
 |
|
|
 |
When a client opens several network printers that are all on a single server and then selects printer properties and preferences on all these printers at the same time, the spooler on the client side may not respond as expected. Additionally, the CPU-utilization of the print server may increase and remain high. In this scenario, a network capture shows that the client repeatedly queries the print server for printer properties.
 |
|
|
 |
When you are using the InterActual DVD playback program that is included with some DVD video titles, you may experience one or more of the following symptoms:
- When you work with the commands on the Options menu, you may not be able to view the extra features (such as the photo gallery) on your DVD.
- After you click a menu, the menu selection light may not be restored.
- After you change the play rate, CPU utilization may increase.
- Menu hotspots may become out of alignment.
|
 |
 |
 |
On your Microsoft Windows XP-based computer, the following failure event appears repeatedly in the security event log:
Source: Security
Type: Failure
Category: Privilege Use
Event ID: 577
Description:
Privileged Service Called:
You may experience slow response times and increased CPU use on your computer when the 577 events occur. If you log on to the Windows XP-based computer with an account that has local administrator credentials, you do not experience these symptoms.
 |
|
|
 |
You may experience one or more of the following symptoms on your Microsoft Windows XP Service Pack 1 (SP1)-based computer or your Microsoft Windows 2000 Service Pack 3 (SP3)-based computer:
- Universal serial bus (USB) devices are not detected when you restart the computer.
- USB devices are not detected after you resume the computer from hibernation or standby.
- The computer uses 100 percent of CPU resources when you move the USB mouse.
- The computer stops responding (hangs) when you resume the computer from standby when a USB mouse is connected.
- The computer takes a long time to start or resume when a USB device is connected.
- A yellow exclamation point with "Code 28" or "Code 31" appears on a USB device in Device Manager.
- USB 2.0 Hi-Speed devices are detected as Full-Speed (USB 1.1) devices when your computer resumes from hibernation, even though they are plugged in to a USB 2.0-capable port.
|
|
|
 |
Assume that you have saved an e-mail message that is 1 megabyte (MB) or larger to your local hard disk from Microsoft Outlook or from Microsoft Outlook Express in HTML format. When you open the HTML file in Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0 Service Pack 1 (SP1) and use Print Preview to view the message before you print it, Print Preview appears to stop responding. Additionally, Print Preview uses 100 percent of CPU resources. If you wait, the preview of the message is eventually displayed in Print Preview. The preview may take several minutes to occur.
 |
|
|
 |
When you use the Remote Shell utility (Rsh.exe) on a computer that is running Microsoft Windows XP with Service Pack 2 (SP2) or Microsoft Windows 2000 with Service Pack 4 (SP4), you may experience one of the following symptoms.
Windows XP with SP2
- You cannot use the command history. Additionally, you receive the following error message:
- Terminal read: The handle is invalid.
- You can use the command history under specific conditions. However, if you use the command history, the Remote Shell utility causes an endless loop. Additionally, if you copy a list of commands to the Remote Shell utility, an endless loop occurs.
Note: When an endless loop occurs, the CPU usage is 100 percent, and the computer is unresponsive.

|
|
|
 |
You cannot install the Media Center Extender for Xbox 360.
You may experience a spike in the CPU usage and a process called DVCSetup.exe is using a high percentage of the CPU.
 |
 |
 |
 |
The problem that the "Symptoms" section describes was corrected in Windows Update Agent 3.0 and in update 927891. These updates were distributed through Microsoft Update in June and July, 2007. If you are still experiencing a problem that resembles the one that this article describes, it may be a different problem. To troubleshoot similar problems, please see the "" section later in this article.
 |
|
|
 |
In Microsoft Windows XP Media Center Edition 2005, when you use the mouse to click Close to quit Gem Master, your computer becomes slow or unresponsive. The Processes tab in Windows Task Manager shows that the Ehshell.exe process uses 100 percent of CPU usage.
 |
|
|
 |
When you try to create a scheduled task by using the Scheduled Task Wizard in Microsoft Windows XP, the wizard stops responding. If you open Task Manager, and then click the Applications tab, the Scheduled Task Wizard is listed as Not Responding. If you click the Processes tab in Windows Task Manager, you find that the Explorer.exe process consumes a high percentage of CPU cycles. The process typically consumes between 96 and 99 percent of the CPU cycles.
 |
|
|
 |
Under stress conditions that involve heavy memory use, a program that was written in Visual C++ may perform better on a computer that is running Microsoft Windows NT 4.0 than on a computer that is running Microsoft Windows 2000 or Microsoft Windows XP.
When you start the program, it seems to have similar or better performance on a computer running Windows 2000 or Windows XP, and then, after physical memory (RAM) is exhausted, the memory manager starts to use the pagefile. When this occurs, the program on the computer running Windows 2000 or Windows XP may slow down compared to the same program on the computer running Windows NT 4.0. When you view the Task Manager on the computer running Windows 2000 or Windows XP, the CPU usage may peak at 100 percent. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
| |
If your high CPU problem started after installing something, uninstall it. If the problem began after uninstalling something, reinstall it.
To eliminate peripherals as the cause of 100% CPU issues in laptops, unplug everything that is plugged into the laptop.
To eliminate hardware as the cause of 100% CPU issues in desktop or tower units, strip the machine down to bare-bones by pulling out all unnecessary cards:
- Remove all cards and peripherals that are not needed to make the machine boot:
- CD drives & DVD drives
- Additional hard disk controllers
- Secondary hard disks
- Sound cards
- TV cards
- Any other non-essential PCI/USB cards
- All USB devices, including hubs
- Add-on serial port cards, etc.
If your desktop or tower has an onboard video card as well as a PCI or AGP card installed, remove the plug-in card and enable onboard video. If you have multiple video cards and no onboard video, remove any PCI video card and keep only the AGP card, if you have an AGP card. You must remove all non-essential cards even if you are 100% convinced that a certain card is not causing the problem.
If you have an internal modem, take it out. If you have an external modem that is plugged into an onboard serial port, disconnect it.
You should be left with a "bare-bones" system with keyboard, mouse, a single video output, a single hard disk and not much else at all.
If the machine operates in this stripped-down mode without running the CPU into the ground then it's fairly certain that one or more of the devices you have removed are the at the root of the problem.
Turn the machine off, put one device only back in and start the machine up again. Repeat this process until the symptoms reappear. If the symptoms do not recur then it's possible that you have put a device back into a different slot to what it was in originally, which means you probably had a device conflict.

|
|
|
 |
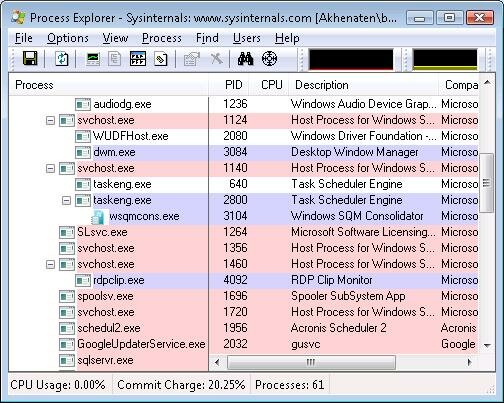
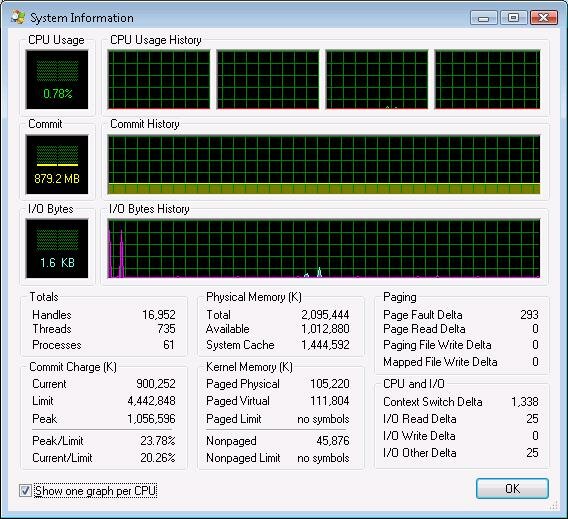
If a SYSTEM process or service host process is going high then you will need to use a tool like Process Explorer to narrow the problem down because service hosts serve more than one process at a time.
Process Explorer Download Link
Shows what program, DLL or service has a file or directory open.
Vista-specific features:
- ASLR column for processes and DLLs
- Process and thread I/O and memory priorities in process and thread properties
- PROCESS_QUERY_LIMITED_INFORMATION support on process permissions
- Run as limited user runs with low IL
- Reports information for all object types
- Show all elevation processes
- Supports replacement of task manager

|
 |
 |
 |
For Advanced high CPU usage troubleshooting, also see:
ADPlus is a tool from Microsoft Product Support Services (PSS) that can troubleshoot any process or application that stops responding (hangs) or fails (crashes). Frequently, you can use ADPlus (ADPlus.vbs) as a replacement tool for the Microsoft Internet Information Server (IIS) Exception Monitor (6.1/7.1) and User Mode Process Dump. These are two separate tools that PSS frequently uses to isolate what causes a process to stop responding (hang) or quit unexpectedy [sic] (crash) in a Microsoft Windows DNA environment.
- What does ADPlus do?
- When should you use ADPlus?
- When should you not use ADPlus?
- Where do you obtain ADPlus?
- How does ADPlus work?
- Hang mode
- Crash mode
- First chance exceptions
- Second chance exceptions
- ADPlus command line switches
- Run ADPlus for the first time
- Typical ADPlus usage scenarios
- Process stops responding or consumes 100 percent CPU utilization
- Process quits unexpectedly
- MTS or COM+ server application quits unexpectedly
- Run in crash mode remotely
In Crash Mode, ADPlus automatically configures the debugger to monitor for the following types of exceptions:
- Invalid Handle
- Illegal Instruction
- Integer Divide by Zero
- Floating Point Divide by Zero
- Integer Overflow
- Invalid Lock Sequence
- Access Violation
- Stack Overflow
- C++ EH Exception
- Unknown Exception
|
|
|
 |
Many issues that you may experience on a Windows XP-based computer occur because of an incompatible or corrupted program. To determine whether this is the case, you can either perform a clean boot or restart Windows without starting the program in question. This article explains how to perform advanced clean-boot troubleshooting to determine whether the problem in question is affiliated with the core operating system or with a program that is loading in the Windows environment.
 |
|
|
 |
This article describes how to troubleshoot configuration errors in Microsoft Windows XP by using the System Configuration utility (Msconfig.exe). Use this tool to modify the system configuration by selecting check boxes to eliminate issues that do not pertain to your configuration.
 |
|
|
 |
Recovery Console and System File Checker
If you cannot resolve the issue by using the startup option, you can use Recovery Console. With the appropriate permissions, you can use this command-line interface to start recovery tools, start and stop services, access files on hard disks, and perform advanced tasks, such as manually replacing corrupted system files. You can run Recovery Console from the Windows XP Professional operating system CD, or you can install it as a startup option.
 |
 |
 |
 |
gives an administrator the ability to scan all protected files to verify their versions. If System File Checker discovers that a protected file has been overwritten, it retrieves the correct version of the file from the cache folder or the Windows installation source files, and then replaces the incorrect file. System File Checker is the main component of the .
 |
|
|
 |
Also see: Turn Off the Indexing Service
There is also a kadaitcha.cx Blog entry that contains pointers to troubleshooting high CPU problems. |
|
|
